Abstract
Background
Recommendations for 2 nd line treatment for relapsed multiple myeloma (MM) patients have been changing over the past two decades, given the introduction of novel agents, different side-effect profiles, and attempts at more individualized treatment approaches. We designed this study to characterize how 2 nd line treatment strategies have evolved over the last two decades for MM patients.
Methods
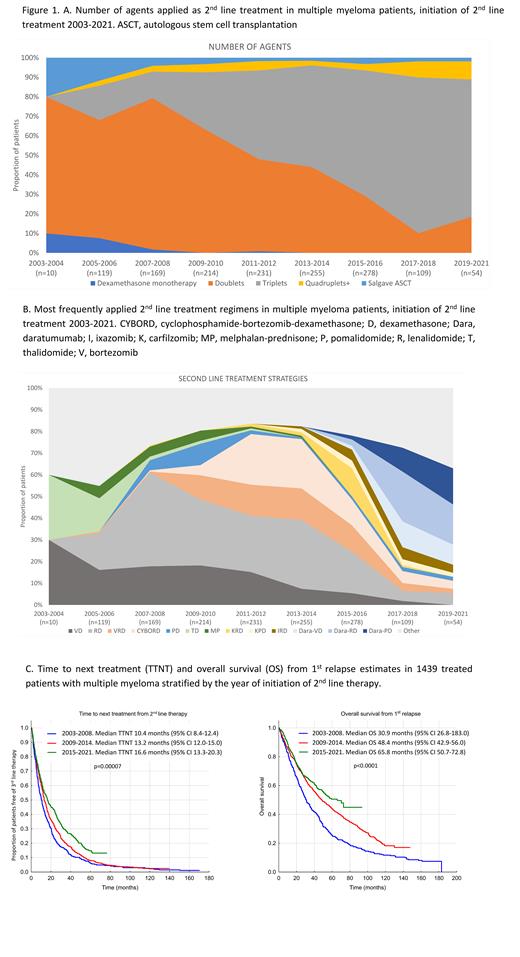
Patients with MM with at least one relapse treated with a 2 nd line regimen, seen at Mayo Clinic between 2003-2021, were included. To visualize trends in treatment choices we divided the study period into 2-year intervals and for descriptive purpose the period was divided into three 6-year intervals. We used "100% stacked area" charts to show how the constituent parts of the whole have changed over time. The height of each colored stack represents the proportion of patients in that category at a given point in time.
Results
A total of 1439 patients were included. Patients were diagnosed between 2001 and 2018, the initiation of 2 nd line treatment occurred between June 2003 and February 2021. Median age at diagnosis was 62.7 years (interquartile range, 55.8-69.3), 60.0% were male. International Staging System stage I was present in 23.5% of patients, stage II in 32.9% and stage III in 28.8%. In the 1 st line therapy novel agents were used in 82.8% of cases, regimens based on proteasome inhibitors (PI) in 26.5%, immunomodulatory drugs (IMID) in 42.0% and combination of PI+IMID in 21.1%. Upfront autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) was performed in 50.1% of patients, and maintenance after 1 st line was used in 25.2%.
For 2 nd line treatment, during 2003-2008 the majority were treated with doublets (70.5%), followed by triplets (14.8%) and salvage ASCT (7.7%) (Figure 1A). Patients were treated with IMID or PI-based therapy (50.7% and 21.8%, respectively); only 3.7% received PI+IMID and 20.1% of patients received alkylating agents/anthracyclines. The most frequently used regimens were lenalidomide-dexamethasone (RD, 32.2%) and bortezomib-dexamethasone (VD, 18.1%, Figure 1B).
Between 2009-2014, the use of triplets in 2 nd line increased (43.0%), although doublets were still more common (50.9%). Like previous years, IMID-based therapy was most frequently used (37.3%), however, the use of PI-based therapy increased (36.0%). PI+IMID-based therapy was implemented in 17.9% of patient, and 27.3% received alkylating agents/anthracyclines. Most frequently used regimens included: RD (29.4%), bortezomib-cyclophosphamide-dexamethasone (CYBORD, 17.4%), bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone (VRD, 13.4%) and VD (13.3%).
Finally, during 2015-2021, triplets were most common (68.9%), followed by doublets (23.0%). IMID- and PI+IMID-based therapies were most often implemented (34.2% and 31.1%, respectively), followed by PI-based therapy (26.8%). 28.1% of patients received monoclonal antibodies; only 15.9% received alkylating agents/anthracyclines. Most frequently used regimens include RD (13.8%), carfilzomib-RD (11.6%), daratumumab-RD (9.8%), CYBORD (9.3%), VRD (8.8%), daratumumab-pomalidomide-dexamethasone (5.9%) and daratumumab-VD (5.2%).
Median time to next treatment (TTNT) from 2 nd line therapy has improved over the course of the three time periods (p<0.01; Figure 1C): years 2003-2008, 10.4 months; years 2009-2014, 13.2 months; and years 2014-2021, 16.6 months. Similarly, the median overall survival from 1 st relapse has increased over the three intervals: 30.9 months, 48.4 months, and 65.8 months, respectively.
Conclusions
Over the past two decades, the effectiveness of 2 nd line treatment has improved, reflected by improved TTNT from 2 nd line therapy. With the introduction of new agents in 2012-2015 (carfilzomib, pomalidomide and daratumumab) and favorable results for triplets demonstrated in randomized trials, the triplet therapies started to be used more frequently. Over time, the landscape of 2 nd line therapies has become more diverse, which may reflect a more individualized approach to each patient. Moreover, the large variety of treatment strategies makes comparisons more and more challenging.
Kapoor: Ichnos Sciences: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; BeiGene: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Amgen: Research Funding; Cellectar: Consultancy; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Glaxo SmithKline: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding. Dispenzieri: Pfizer: Research Funding; Alnylam: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Sorrento Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding. Gertz: Akcea Therapeutics, Ambry Genetics, Amgen Inc, Celgene Corporation, Janssen Biotech Inc, Karyopharm Therapeutics, Pfizer Inc (to Institution), Sanofi Genzyme: Honoraria; Aurora Biopharma: Other: Stock option; Akcea Therapeutics, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc, Prothena: Consultancy; AbbVie Inc, Celgene Corporation: Other: Data Safetly & Monitoring; Ionis Pharmaceuticals: Other: Advisory Board. Dingli: Sanofi: Consultancy; Apellis: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy. Kumar: Adaptive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Tenebio: Research Funding; Carsgen: Research Funding; Beigene: Consultancy; Antengene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche-Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Astra-Zeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; KITE: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal